1️⃣Associations
A social network can be visualized as an undirected graph with users and posts acting as nodes and their interactions acting as the edges connecting them.
An “association” is a transaction type on the DeSo blockchain to embody those edges to help connect this graph.
There are two types of associations:
User associations
Post associations
And in total, we've introduced 4 new distinct transaction types on the DeSo blockchain to support associations:
CREATE_USER_ASSOCIATION
DELETE_USER_ASSOCIATION
CREATE_POST_ASSOCIATION
DELETE_POST_ASSOCIATION
A simple way to think of this relationship is that 1) user associations connect a user (the transactor) to another user (the target user), and 2) post associations connect a user (the transactor) to a post (the target post).
In addition to the transactor and the target user or post, associations have three customizable fields:
The association type
The association value
The application scope
The association type allows associations to be a polymorphic data structure, representing multiple different kinds of relations between users and other users or users and posts.
The application scope allows an association to be specified either within the scope of a single application or globally across all applications on the DeSo blockchain.
User Examples
Associations are easiest explained using a few example use-cases.
Let’s start with user associations.
User associations can be used to endorse other users, similar to the skills endorsement feature available on LinkedIn.
Imagine User A wants to endorse User B for knowing the programming language “JavaScript” on Diamond.
User A can submit the following association transaction:

This association acts as an official on-chain endorsement by User A of User B’s knowledge of “JavaScript”.
This is non-spoofable because, like all transactions on the DeSo blockchain, User A will have to sign that payload with his private key for it to be accepted.
This allows applications built on top of the DeSo blockchain to then query using the DeSo API for all of the users who User A has endorsed or all of the users who have endorsed User B for knowing JavaScript.
Other user association use-cases we have in mind that are now enabled include reporting users, flagging users, blocking users, user stats & scoreboards, and provable / gateable group membership. We’ll talk more about this later.
Post Examples
Let’s also consider an example post association. Currently, the DeSo blockchain allows for a user to submit a LIKE transaction to “thumbs up” a post. However, Associations will allow them to submit any reaction on a post.
For example, imagine User A would like to HEART User B’s post globally across all applications. Or maybe react with a thumbs-up, an upvote, a downvote, a smiley face, a crying face, or any other popular emoji.
User A can submit the following association transaction:
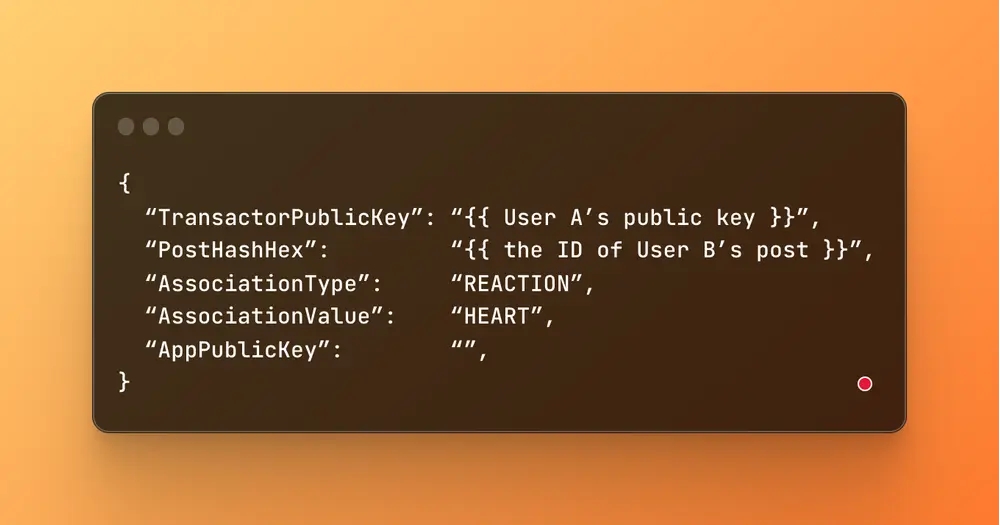
Applications built on top of the DeSo blockchain can query for the number of reactions on User B’s post, all of the users who have hearted the post, etc.
Other post association use-cases we have in mind that are now enabled include flagging posts, reporting posts, and tagging posts as e.g. NSFW.
One could imagine a Reddit clone now being built on top of the DeSo blockchain leveraging user associations to specify moderators and post associations for those moderators to tag posts by their subreddit.
And best of all, all of the other DeSo features come for free like single sign-on, tipping, NFTs, DeSo Tokens, the DeSoDollar stable coin, etc.
Infinite Use-Cases
Notice that the association type and association value attributes of an association can be any user-defined string. So there are infinite possibilities for associations beyond the examples described above.
And the DeSo API allows for advanced querying to slice-and-dice on-chain associations to power all kinds of applications.
In this way, with a single new transaction type on the DeSo blockchain, we have enabled infinite new possibilities for storing generic key-value data relating users and posts on-chain, all for very cheap as DeSo boasts incredibly low transaction fees.
Let’s take a look at even more concrete examples of how associations can be used:
Reactions
Currently, users can LIKE a post, but associations now enable apps to allow any arbitrary reaction on a post such as thumbs up, thumbs down, happy face, heart emoji, laughing face, crying face, etc.
Association Class: User
Transactor: The user doing the reacting
Target Post: The target post being reacted on
Association Type: REACTION
Association Value: THUMBS_UP | THUMBS_DOWN | HEART | LAUGH | CRY …
App: Can optionally scope post reactions to a single app
Moderators
Associations can be used to assign moderators of an application. They can more generically be used to build out an entire on-chain application’s roles-rights permission system.
Association Class: User
Transactor: The app’s public key
Target User: The user being granted permission
Association Type: ACCESS_ROLE
Association Value: ADMIN | LEVEL_1 | LEVEL_2 | LEVEL_3 …
App: App’s public key
Tagging Posts
Associations can be used to arbitrarily tag posts. These tags can then be used to sort + moderate content.
Association Class: Post
Transactor: The user doing the tagging
Target Post: The post being tagged
Association Type: TAG
Association Value: NSFW | Sports | Business | Technology …
App: Can optionally scope post tags to a single app
Subreddits
Combining the moderator and tag use-cases above can enable an on-chain Reddit clone. Users can submit posts and tag them as belonging to a specific subreddit, e.g. r/bitcoin
The app can assign moderators who can then perform some admin functionality like blacklisting posts or users. And users can upvote or downvote posts within each subreddit.
Reporting, Flagging, Blocking Users
Associations allow for users to report, flag, or block other users. Applications can then use this information to e.g. block a user from the app if enough individual users report.
Association Class: User
Transactor: The user doing the reporting, flagging, blocking
Target User: The user being reported, flagged, blocked
Association Type: REPORT | FLAG | BLOCK
Association Value: This can optionally provide a reason for reporting, flagging, or blocking
App: Can optionally scope the action to a single app
Reporting, Flagging, Hide Posts
Associations allow for users to report, flag, or hide posts. Applications can then use this information to e.g. hide posts.
Association Class: Post
Transactor: The user doing the reporting, flagging, or hiding
Target Post: The post being reported, flagged, or hidden
Association Type: REPORT | FLAG | HIDE
Association Value: This can optionally provide a reason for reporting, flagging, or hiding
Facebook-Style Friend Requests
Associations enable applications to allow for users to send friend requests to each other. The application can then query if a user is a friend and can gate content to e.g. only-friends, or close friends, etc.
1. Friend Request
Association Class: User
Transactor: The user requesting the friendship
Target User: The user whose friendship is being requested
Association Type: FRIEND_REQUEST
Association Value: REQUEST
App: Can optionally scope a friend request to a single app
2. Friend Request Approval
Association Class: User
Transactor: The user who is approving an existing friend request
Target User: The user who originally requested the friendship
Association Type: FRIEND_REQUEST
Association Value: APPROVE
App: Can optionally scope a friend request approval to a single app
Instagram-Style Follow Request
Following the exact REQUEST → APPROVE pattern for Facebook-Style Friend Requests above, associations allow for users to submit and approve follow requests.
Applications can gate content to only their followers.
The association looks identical to the above except the association type would be FOLLOW_REQUEST instead of FRIEND_REQUEST.
Facebook-Style Groups
Associations allow for users to create groups and then gate who gains access to that group. Users can even submit requests to be considered to be allowed in.
Association Class: User
Transactor: The owner of the group
Target User: The user being allowed into the group
Association Type: GROUP_MEMBERSHIP
Association Value: The group name, e.g. Harvard University Alumni
App: Can optionally scope group memberships to a single app
LinkedIn-Style Endorsements
Associations allow for users to endorse other users for specific skills, exactly like the feature on LinkedIn.
Association Class: User
Transactor: The user doing the endorsement
Target User: The user they are endorsing
Association Type: ENDORSEMENT
Association Value: The skill they are being endorsed for, e.g. SQL | JavaScript | Marketing | Public Speaking
App: Can optionally scope endorsements to a single app
Polls
Associations allow for users to submit a post with poll options and then users to submit their poll response.
Association Class: Post
Transactor: The user responding to a poll
Target Post: The post which contains the poll
Association Type: POLL_RESPONSE
Association Value: The poll response, e.g. YES | NO
App: Can optionally scope poll responses to a single app
Game Scoreboards
Associations allow for games to store their daily user leader scoreboards on-chain.
For example, consider a daily Wordle challenge where the game wants to store the user and how many tries it took them to guess the word to then display a daily leader scoreboard.
This is possible with associations:
Association Class: User
Transactor: The game app’s public key
Target User: The user who received the high score
Association Type: 2023-01-26_HIGH_SCORE
Association Value: Their score, e.g. 4
App: The game app’s public key
DeSo will introduce a set of recommended standards for applications to reference. We hope this demonstrates the power of what associations can achieve and we can’t wait to see what new possibilities developers unlock.
Last updated
Was this helpful?
